Μελισσοκομικά Εφόδια

Κυψέλη ξύλινη κομπλέ
• 10 πλαισίων
• 8 πλαισίων
• 5 πλαισίων
Καθώς επίσης Τριπλοκυψελίδια, Μεσοπατώματα, Κινητές βάσεις κλειστές ή με σίτα (ξύλινες, πλαστικές), Πλαίσια (συρματωμένα ή με κηρήθρα).

Κηρήθρες
- Κηρήθρες 78-80 gr ,απο 100% φυσικό κερί, σε συσκευάσια 80 τεμ.
- Kηρήθρες βαρέου τύπου,από 100% αγνό κερί σε συσκευασία 100 τεμ.
- Κηρήθρες γαλλικές ,από 100% φυσικό κερί,
- σε συσκευασία 64 τεμ.

Πλασιοδιάφραγμα βασιλισσών
(1,2,3 πλαίσια)
Honeycomb Electrical Embedder

Αρμοστήρας κηρηθρών ηλεκτρικός

Σύρμα πλαισίου 2kg
• No 24
• No 25
• No 26
Σύρμα κουλούρα μαλακό 1kg

Καψούλια πλαισίων νίκελ
- συσκευασία 1000 τεμαχίων
Συσκευή συρμάτωσης και κερώματος πλαισίων

Τραπεζάκι τεντώματος σύρματος

Φλόγιστρο για καθαρισμό και απολύμανση των κυψελών

Βούρτσα τρυγητού με φυσική τρίχα

Τάπα κυψέλης πλαστική μαύρη

Συνδετήρας κυψέλης ρυθμιζόμενος κομπλέ

Συνδετήρας κυψέλης ρυθμιζόμενος κομπλέ.Καθώς επίσης συνδετήρας έλασμα για κινητή βάση και για κυψελίδια.

Hive HandleΧειρολαβή κυψέλης

Καπνιστήρι δερμάτινο ή δερματίνη με ή χωρίς πλέγμα

Καψουλίερα

Πυροσφραγίδα και ορειχάλκινοι αριθμοί

Γυρεοσυλλέκτης πλαστικός

Μαχαίρι απολεπισμού ,ηλεκτρικό inox με ρυθμιστή θερμοκρασίας.Καθώς επίσης μαχαίρι απολεπισμού inox απλό ,πριονοτό ή ατμού

Πιρούνι ξεσφραγίσματος κηρήθρας inox

Φίλτρο μελιού με διπλή σίτα inox

Μελιτοεξαγωγέας inox χειροκίνητος ή ηλεκτρικός:
- 2 πλαισίων
- 4 πλαισίων
- 6 πλαισίων
- 8 πλαισίων
- 10 πλαισίων

Δοχείο μελιού ανοξείδωτο :
- 50 kg
- 75 kg
- 100 kg
- 150 kg
- 200 kg

Ξέστρο :
- ατσάλινο τύπου Αυστραλίας
- κλασσικό ατσάλινο
- σίδερο σφυράκι
- κίτρινο κοντό ή μακρύ
Καθώς επίσης ξέστρο καθαρισμού πλαισίου
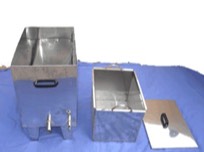
Κηροτήκτης ατμού inox
Κηροτήκτης ηλιακός

Τροφοδότης οροφής πλαστικός μαύρος 7,5 kg

Τροφοδότης οροφής πλαστικός διάφανος 7,5 kg.Καθώς επίσης τροφοδότης πλαστικός τάπερ 1,5 lt.

Τροφοδότης οροφής σήτα 2,5 kg

Τροφοδότης πλαισίου με πλωτήρες 1,5 kg και 3 kg.

Δαγκάνα πλαισίου
Δαγκάνα πλαισίου με ξέστρο κίτρινη

Σήτα συλλογής πρόπολης καφέ

Σφηκοπαγίδα συρμάτινη φορητή
Σφηκοπαγίδα
Δακοπαγίδα
Καθώς επίσης Σκουρκοπαγίδα κώνος με μεταλλική σήτα.

Διάφραγμα βασίλισσας μεταλλικό
Διάφραγμα βασίλισσας πλαστικό

Πάγκος απολεπισμού με καπάκι inox 13 ,25 πλαισίων

What is Apiculture?
Apiculture is the management and study of honeybees.
Apiculture is the management and study of honeybees.
Apiculture is derived from the honeybee's Latin name Apis mellifera, meaning ‘honey gatherer’. Since bees do not collect honey but nectar from which honey is made, the scientific name should actually be Apis mellifica meaning ‘honey maker’.
Although apiculture refers to the honeybee, the vital role all bees play in the pollination of crops and flowering plants has caused apiculture to also include the management and study of non-Apis bees such as bumblebees and leafcutter bees.
Some 90 million years ago, flowering plants first appeared on earth. The wasp-like ancestors of bees took advantage of the food made available by flowers and began to modify their diet and physical characteristics.
Since then, flowering plants and bees co-evolved. This eventually led to a complete interdependence, meaning that flowering plants and bees cannot live and reproduce without each other.
Since then, flowering plants and bees co-evolved. This eventually led to a complete interdependence, meaning that flowering plants and bees cannot live and reproduce without each other.
The genus Apis is comprised of a comparatively small number of species including the western honeybee Apis mellifera, the eastern honeybee Apis cerana, the giant bee Apis dorsata, and the small honeybee Apis florea.
Honeybees are indigenous to the Eurasian and African continents and were introduced to the Americas and Australia by European settlers.
The western honeybee is comprised of some 24 races or sub-species. The African honeybee, sometimes referred to as ‘Killer bee’, is a race of the western honeybee and can therefore cross-breed.
Bees collect pollen and nectar. Pollen is the protein source needed for bee brood development while nectar is the carbohydrate source providing energy.
Nectar is a sugar solution produced by flowers containing about 80% water and 20% sugars. Foraging bees store the nectar in the ‘honey sac’ where the enzyme invertase will change complex sugars into simple sugars called mono-saccharides. Upon return to the hive, the foraging bee will disgorge the partially converted nectar solution and offer it to other bees. Housekeeping bees will complete the enzymatic conversion, further removing water until the honey solution contains between 14 – 20% water.
Honey is too dry for any microbes to live in. Honey is non-perishable and can be kept indefinitely in a cool, dry place.
The flavor, aroma and color of honey is determined by the floral source. For example, buckwheat honey is almost black while fireweed honey is almost colorless.
Unlike other bees, honeybees can communicate details about the location, quality and quantity of food sources. This allows honeybees to access and utilize food sources efficiently at great distances.
Honeybees maintain temperatures in the brood nest of between 30º C and 34º C, even in the middle of winter.
The honeybee colony is comprised of one queen, thousands of worker bees and a few hundred male bees called drones. Colony size varies according to season and condition of the colony.
Several diseases including viruses, various microbes and mites can affect the honeybee.
Honeybees are used in pollination and play a critical role in the production of many crops, representing a value of over $14 billion per year in North America.










